“Early detection, rapid response, and public awareness are the strongest tools we have to control deadly viral outbreaks.”
The Nipah virus outbreak is a serious public health concern due to its high fatality rate and potential for human-to-human transmission. Identified as a priority pathogen by the World Health Organization, Nipah virus infections can lead to severe respiratory illness and fatal brain inflammation. Understanding how the virus spreads, recognizing early symptoms, and following evidence-based prevention strategies are critical for protecting individuals and communities.
What Is the Nipah Virus?
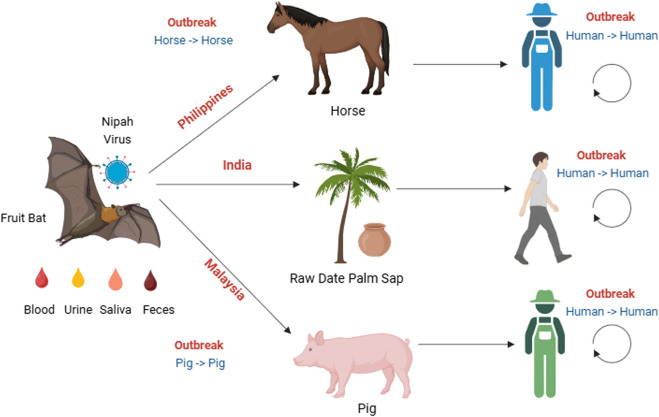
The Nipah virus (NiV) is a zoonotic virus, meaning it spreads from animals to humans. Fruit bats of the Pteropus species are the natural carriers, and the virus can also infect pigs and other animals. Since its first recorded outbreak in 1999, Nipah virus cases have been reported mainly in South and Southeast Asia, often linked to contaminated food or close contact with infected individuals.
Health Impact and Why It Matters
Nipah virus infection is associated with a high mortality rate, ranging from 40% to 75% depending on outbreak response and healthcare access. Survivors may experience long-term neurological complications, making early detection and containment essential for public health safety.
Common Symptoms of Nipah Virus Infection
Symptoms usually appear within 4 to 14 days after exposure and may worsen rapidly. Common signs include fever, headache, muscle pain, vomiting, and sore throat. In severe cases, patients can develop acute respiratory distress, seizures, and encephalitis (brain swelling), which can lead to coma or death.
Causes and Transmission
The Nipah virus spreads through direct contact with infected animals, consumption of contaminated food such as raw date palm sap, or close contact with bodily fluids of infected people. Human-to-human transmission has been documented, particularly in healthcare and family settings, making infection control measures crucial during outbreaks.
Prevention and Risk Reduction Strategies
Currently, there is no approved vaccine or specific antiviral treatment for Nipah virus infection. Prevention focuses on reducing exposure and limiting transmission. Avoid consuming raw or unprocessed foods that may be contaminated by bats, practice strict hand hygiene, and use protective equipment when caring for infected individuals. Healthcare facilities must follow standard infection control protocols to prevent spread.
Lifestyle and Health Protection Tips
Maintaining a strong immune system through balanced nutrition, adequate sleep, stress management, and regular physical activity can support overall health, although these measures do not replace preventive infection control. Staying informed through trusted health authorities and seeking early medical care when symptoms appear are vital steps during an outbreak.
Conclusion: The Nipah virus outbreak highlights the importance of early awareness, strong public health systems, and individual responsibility. While the virus poses serious health risks, informed prevention, prompt medical care, and adherence to safety guidelines can significantly reduce transmission and save lives. Staying educated through credible sources remains the most powerful tool in protecting yourself and your community.
#NipahVirus #NipahOutbreak #PublicHealth #HealthAwareness #InfectiousDiseases #VirusPrevention #HealthSafety #DiseaseControl #WHO #HealthNews #Anslation #Carrerbook
FAQ’s ?
When should I seek medical help?
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience fever, headache, or respiratory symptoms after possible exposure.
How can I protect myself during a Nipah virus outbreak?
Avoid exposure to potentially contaminated food, practice good hygiene, and follow public health guidelines issued by authorities.
Is there a vaccine for Nipah virus?
Currently, there is no approved vaccine, though research and clinical trials are ongoing.
What is the fatality rate of Nipah virus infection?
The fatality rate ranges from 40% to 75%, depending on outbreak response and healthcare availability.
Is the Nipah virus contagious?
Yes, Nipah virus can spread from person to person through close contact with bodily fluids, especially in healthcare or household settings.
Medical Disclaimer: This content is for informational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider for medical concerns or symptoms.